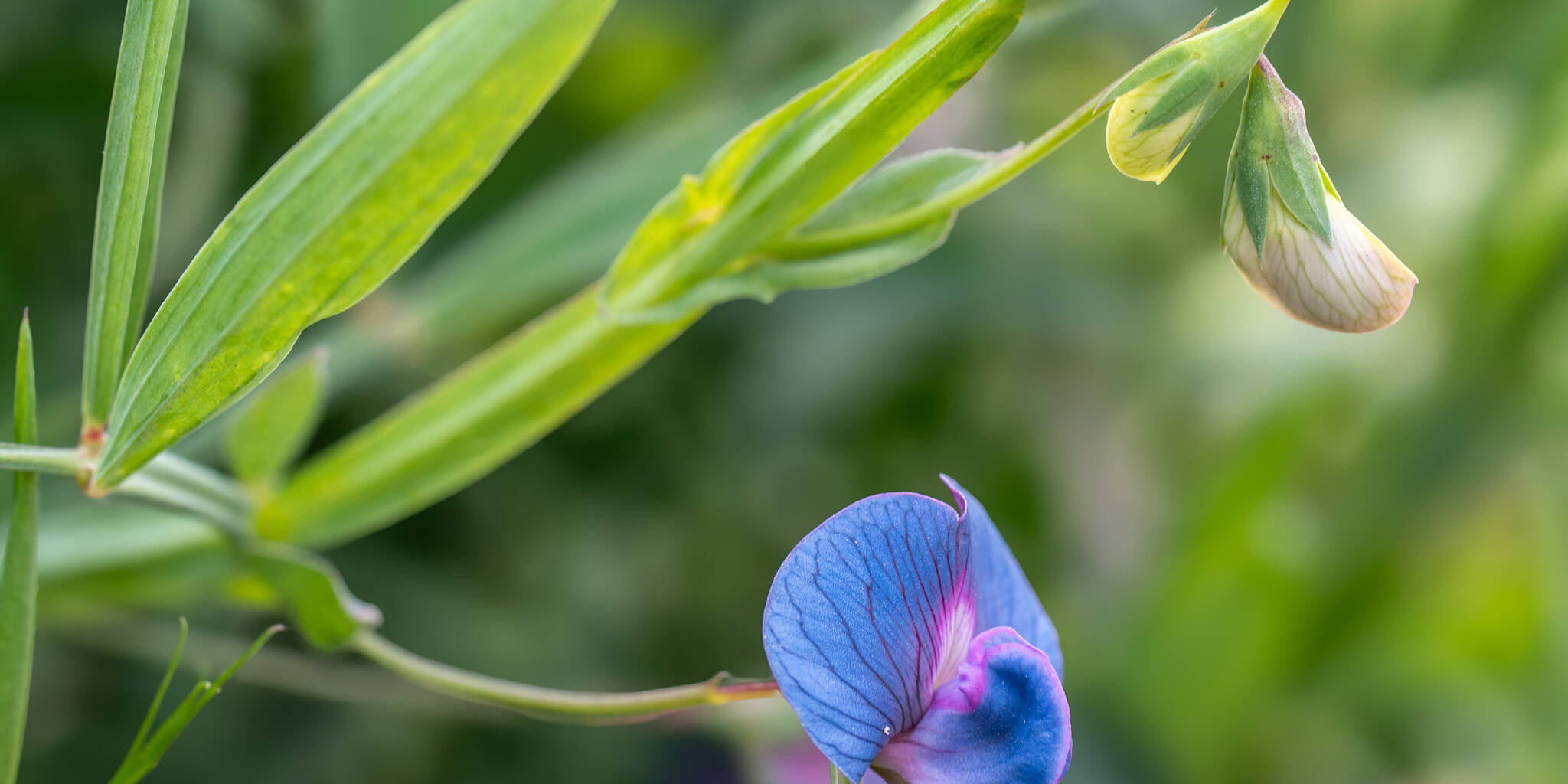
When I started writing on grasspea, I came across many special names and striking phrases of this amazing legume crop, which not only caught my attention but forced me to write the acronym of GRASSPEA and LATHYRUS. These acronyms not only give the collective impression of this miraculous plant but also capture my attention to its value as a functional food. Grasspea is a common name and here, I provide general description of its acronym based on its general features suggested by farmers and consumers. In the same way, Lathyrus is its botanical name which will explain scientific assets of grasspea reported by scientists.
‘GRASS of Grasspea’ is the first in the series on Incredible Grasspea which will be followed by ‘PEA of Grasspea’, ‘LATHYRUS: Scientific acronym of Grasspea’, ‘Fancy findings of Grasspea’, My relationship with Grasspea, ‘Scientists’ views on Grasspea’, ‘Consumers on Grasspea’ and at last ‘ICARDA and Grasspea’.
This series has been written by Dr Priyanka Gupta please follow them on Twitter @VidhiPriyanka
Incredible Grass pea
How many times we have discussed feeding 9.9 billion people by 2050, but then again, do we just need to feed? Is this the only issue in agriculture research? don’t we have to work for nutritious and healthy food, and not only nutritious food but also to mitigate environmental challenges, improve soil quality, improve biodiversity and adoption of the orphan (diverse) crops with its incredible potential. Based on the above requisite, here I provide the general description of the ‘PEA of grasspea’ which mainly focus on nutritional quality, ecosystem services and its adoption as a diverse legume crop.
P: Poisonous poor man’s pulse to Panacea grass pea
What is Poison? According to Paracelsus (famous physician) ‘Poison is in everything, and nothing is without poison. The dosage makes it either a poison or a remedy. If I talk ‘Poison’ being the dose – everything has poison, for instance, sugar is poison for diabetic people, certain cereals (wheat, barley and rye etc.) are poison for Celiac people, and for obese people, high calorie, processed and fast food is poison. What is food for one person may be bitter poison to others so the frequent statement was written for grasspea; ‘excessive consumption as a staple food during a prolonged periods’- Not many food groups would pass that test without affecting health?
On the brighter side, grasspea as a ‘Panacea crop’ has a lot to offer; firstly, gasspea contains 30% protein, and more than 17% total dietary fiber. its protein content is higher compared to other pulse crops. Secondly, the presence of homoarginine and its contribution as a better substrate for Nitric Oxide (NO) production receiving conscious attention. Nitric Oxide is key compound to treat cardiac disorders, Alzheimer’s disease, hypoxia and long-term potentiation. Hence, a regular dietary consumption of homoarginine through small quantities of grasspea is helpful for general well-being. ICARDA is investigating in depth to enhance the nutritional status of grasspea. These novel therapeutic potentials and its nutritional value might completely change the old perception of ‘poisonous poor man’s pulse to panaceas grasspea’.
E: Ecosystem services of grasspea
Sustainable use of earth and environment is a global challenge in today’s time. Imagine the earth as router and environment as Wi-Fi signals, then we would probably take its best care and save the planet. Unfortunately, it is only a great connector of lives we live and produce oxygens we breathe. Maurice said ‘A shift is required toward a lifestyle less geared to environmental damaging consumption patterns’. Beside that we certainly need valuable agricultural crops that keep people and planet healthy and safe.
There are various reasons to say why grasspea is one of the environment friendly and robust legume. First and foremost, its ability to withstand adverse climatic and soil conditions, the hardy penetrating root system architecture permits to extract moisture from sandy clay soils, including marginal ones. Moreover, to escape drought, grasspea plant matures early and survive under terminal desiccation. Second, grasspea as plant-based protein is highly appreciated for cheap meat replacement, particularly in poorer counties and for people who follow vegetarian régimes. The third and important factor its ecological properties, grasspea as an efficient nitrogen fixer, fulfills its own nitrogen requirements and positively assist subsequent crops and enriches soils.
In today’s world, it is acknowledged that ‘protein’ and ‘meat’ are not synonym and plant-based protein reduce water footprint by up to 55% thus plant-based food is dietary preference. When we think to grow a plant- based protein in water-limited condition, in various soil types and in extreme environments, grasspea provides holistic system approach that promote continual on-farm improvement for environmental, social and economic wellbeing, thus, it has featured as a superior legume crop for ecological services.
A: Orphan to Adoption of grass pea
Grasspea is easier to ignore before you know its functional aspects. It may not sound acquainted to several people and have least recognition. it is not traded internationally and considered inferior crops in term of agricultural training and research network. Certainly, Grasspea is considered minor and most orphan legume crop. But the question is? Was grasspea really orphan or neglected crop? If we see the history, grasspea is that plant whose virtues discovered by our Neolithic ancestors when farmers came in existence, it is not only lived millennia of cultivation but has spread over several continents. Grasspea was considered as a superior food to be offered to emperors and found in funeral ceremonies in the Egyptian pyramids. During the World War II in European countries (Spain, Greece and Portugal), grasspea was used as a feed, food and fodder, in contrary to the modern reputation of being the survival food for deprived people. Sadly, in the same land now it is a nearly forgotten crop, just planted in a few small plots to be consumed mainly during some religious formalities.
The overfeeding of grasspea in diets during starvation has given it its existing undeserved rank of being a toxic plant. Due to this stigma, efforts to improve grasspea varieties are limited and, hindering its potential exploitation in crop breeding. Although drought-caused famine and a crippling neurological disorder caused by excessive consumption of grasspea has happened three decades back which only restricted to rural areas. Yet, the poorest people are most vulnerable to global climate change and nutritional security thus, grasspea is adopting and evolving as a climate-smart crop that holds a tremendous potential of multiple stress-tolerance. Additionally, it dignified as survival food for subsistence farmers living on marginal lands and, people who struggle to feed their family the most basic foods under harsh conditions.
Written by Dr Priyanka Gupta from ICARDA. Follow Priyanka on Twitter @VidhiPriyanka